Ever felt like your eyes were playing tricks on you? Welcome to the world of astigmatism! Don’t worry, it’s not as scary as it sounds. In fact, it’s common. Let’s dive into the blurry, wiggly world of astigmatism together.
Imagine looking through a funhouse mirror. That’s what astigmatism vision is like. Things may look warped or fuzzy. But don’t fret! We’re here to clear things up.
Are you squinting at street signs? Getting headaches after reading? These could be astigmatism symptoms. But how do you know for sure? That’s where an astigmatism test comes in. It’s quick, painless, and can give you answers.
The good news? There are lots of astigmatism treatment options. From glasses to contacts, we’ve got you covered. So please sit back, relax, and let’s explore the ins and outs of astigmatism.
Table of Contents
- What is Astigmatism?
- Astigmatism Symptoms
- How Astigmatism Affects Your Vision
- Types of Astigmatism
- Causes of Astigmatism
- Diagnosing and Treating Different Types of Astigmatism
- 5 Practical Tips for Living with Astigmatism
- 4 Myths About Astigmatism
- Conclusion
What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a common refractive error, which means the eye does not bend light correctly.
In a normal eye, the cornea and lens are smooth and evenly curved. This shape allows light to focus directly on the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. When light focuses properly on the retina, you see clear images.
In an eye with astigmatism, the cornea or lens is curved more steeply in one direction. This irregular shape causes light to focus on multiple points in the eye. As a result, vision becomes blurred or distorted.
The severity of astigmatism can vary. Some people have mild astigmatism and may not notice significant vision problems. Others have more severe astigmatism and experience more pronounced symptoms.
Astigmatism Symptoms

Astigmatism can cause various symptoms. The most common symptom is blurred or distorted vision. This blurriness can occur at any distance, affecting both near and far vision.
Other common astigmatism symptoms include:
- Eyestrain: The eyes may feel tired or strained, especially after reading or using a computer for long periods.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches can result from the eyes working harder to focus.
- Difficulty Seeing at Night: Low light conditions can make it harder to see clearly, leading to poor night vision.
- Squinting: Squinting is a common response to blurred vision, as it can temporarily improve focus.
- Double Vision: In some cases, astigmatism can cause double vision, where two images of a single object are seen.
These symptoms can vary in intensity. Some people with mild astigmatism may not notice any problems. Others with more severe astigmatism may find these symptoms more pronounced and disruptive to daily activities.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to have an astigmatism test during a comprehensive eye exam.
How Astigmatism Affects Your Vision
Astigmatism affects vision by causing light to focus on multiple points in the eye. This leads to blurred or distorted images.
People with astigmatism may see straight lines as wavy or blurred. They may also have trouble seeing fine details. Astigmatism’s distortion can affect various activities, such as:
- Reading: Letters and words may appear blurry or jumbled, making reading difficult.
- Driving: Blurred vision can make it hard to read road signs, judge distances, or see clearly at night.
- Using a Computer: Extended screen time can lead to eyestrain and difficulty focusing on text or images.
- Recognizing Faces: Faces may appear blurred or distorted, making it challenging to identify people from a distance.
Types of Astigmatism
There are different types of astigmatism. Each type uniquely affects vision.
Myopic Astigmatism
Myopic astigmatism occurs when one or both principal meridians of the eye are nearsighted. In simple terms, this means that distant objects appear more blurred than near objects. The cornea or lens is shaped in such a way that light focuses in front of the retina in one or both meridians.
This type of astigmatism can make driving or recognizing faces from a distance challenging. People with myopic astigmatism may notice that their vision slightly improves as they bring objects closer. Regular eye exams and an astigmatism test can help diagnose this condition.
Eyeglasses or contact lenses are common treatments for myopic astigmatism, providing clearer vision for distant objects.
Hyperopic Astigmatism
Hyperopic astigmatism happens when one or both principal meridians are farsighted. So, near objects appear more blurred than distant ones. In this type, the cornea or lens causes light to focus behind the retina in one or both meridians.
Reading, sewing, or using a smartphone can be difficult for people with hyperopic astigmatism. They might hold reading materials further away to see clearly. Regular eye exams and an astigmatism test can identify hyperopic astigmatism.
Eyeglasses or contact lenses can correct this type, helping to bring near objects into clearer focus.
Mixed Astigmatism
Mixed astigmatism is a combination of myopic and hyperopic astigmatism. In this type, one principal meridian is nearsighted, and the other is farsighted. This causes a combination of blurred vision at different distances.
For instance, someone with mixed astigmatism might find both reading a book and seeing a distant sign difficult. The vision distortion can be more complex, making everyday tasks challenging. An astigmatism test can diagnose mixed astigmatism.
Treatment usually involves eyeglasses or contact lenses designed to correct both meridians. In some cases, refractive surgery might be considered.
Causes of Astigmatism

Astigmatism is usually present at birth, meaning many people have it from a young age. Genetics play a significant role in astigmatism. If your parents have astigmatism, you are more likely to have it too.
However, astigmatism can also develop later in life. Here are some common factors that can contribute to astigmatism:
Eye Injuries
An injury to the eye can alter the shape of the cornea, leading to astigmatism. Even a minor injury can cause scarring or changes in the cornea’s curvature. Such injuries can result in astigmatism symptoms like blurred vision and eyestrain.
If you experience an eye injury, it is important to see an eye doctor. They can perform an astigmatism test to determine if the injury has affected your vision.
Eye Surgery
Eye surgery, such as cataract removal, can sometimes lead to astigmatism. During surgery, the cornea can change shape, causing astigmatism symptoms. Surgeons often use special techniques to minimize this risk.
However, some patients may still develop astigmatism after surgery. If this happens, your eye doctor can recommend astigmatism treatment options to improve your vision.
Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a condition where the cornea becomes thin and cone-shaped. This abnormal shape can cause severe astigmatism. Keratoconus usually begins in the teenage years and progresses over time. It can lead to significant vision problems if not treated.
Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and management. Treatments for keratoconus include special contact lenses or surgery to stabilize the cornea.
High Myopia (Nearsightedness)
People with high myopia, or nearsightedness, are at a greater risk of developing astigmatism. In high myopia, the eyeball is longer than normal, causing light to focus in front of the retina.
This elongation can also affect the shape of the cornea, leading to astigmatism. Regular eye exams can help detect changes in vision and provide appropriate astigmatism treatment.
High Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
High hyperopia, or farsightedness, can also contribute to astigmatism. In hyperopia, the eyeball is shorter than normal, causing light to focus behind the retina. This condition can lead to changes in the cornea’s shape, resulting in astigmatism.
People with high hyperopia should have regular eye exams to monitor their vision and receive suitable astigmatism treatment.
Diagnosing and Treating Different Types of Astigmatism
Diagnosing the type of astigmatism involves a comprehensive eye exam. During the exam, an eye doctor will perform an astigmatism test using various tools. They might use a phoropter to measure how light focuses on your retina and a keratometer to assess the curvature of your cornea. Identifying the specific type of astigmatism is crucial for determining the best treatment.
Importance of Astigmatism Testing
An astigmatism test is crucial for identifying and managing the condition. Regular eye exams are essential to monitor changes in vision and adjust treatments as needed. Detecting astigmatism early can prevent worsening symptoms and improve overall eye health.
Blurred vision, eyestrain, and headaches can all be signs of astigmatism. If you experience these symptoms, see an eye doctor for a comprehensive exam. Proper diagnosis through these tests ensures effective astigmatism treatment.
Different Types of Astigmatism Astigmatism Tests
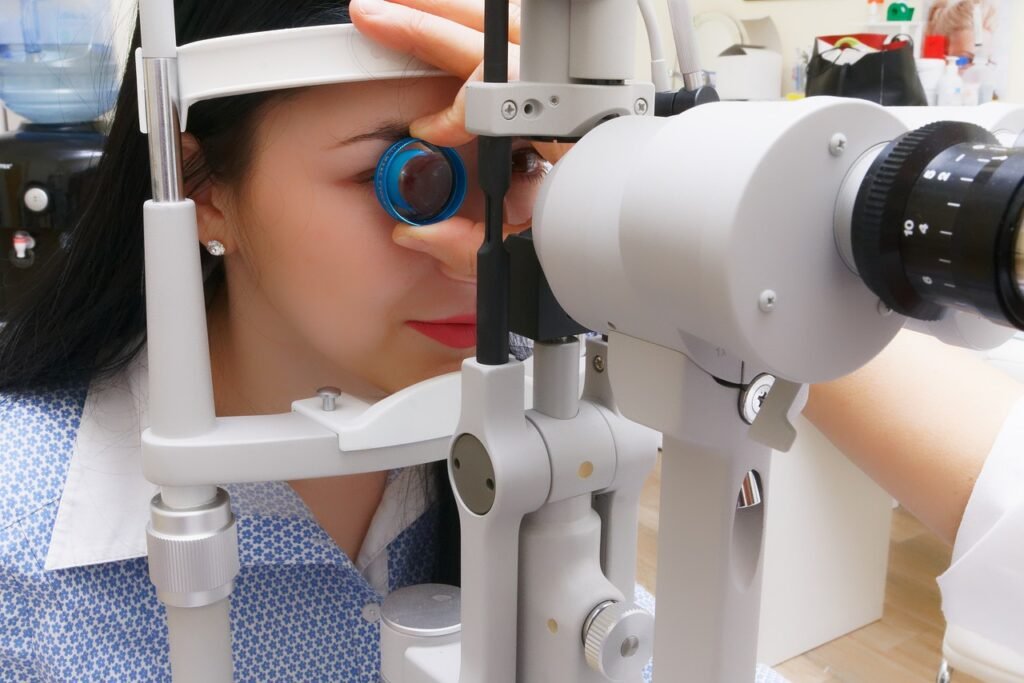
An astigmatism test is part of a comprehensive eye exam. During the exam, the eye doctor will use various tools to measure how the eye focuses light. Here are some common tests used:
Visual Acuity Test
The visual acuity test measures how well you see at various distances. This test is straightforward. You will read letters on a chart, both near and far. The chart typically starts with large letters at the top and gets smaller toward the bottom.
The eye doctor will ask you to cover one eye at a time while reading the letters. Helps determine if you have any vision problems, including astigmatism. Blurred vision or difficulty reading certain lines can be an indicator of astigmatism symptoms.
Keratometry
Keratometry measures the curvature of the cornea. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped surface of the eye. In this test, you will look into a device called a keratometer. The device shines light on the cornea and measures the reflection. This measurement helps the eye doctor understand the shape of your cornea.
An irregular curvature can indicate astigmatism. Keratometry is a quick and painless test. It provides essential information for diagnosing astigmatism and planning astigmatism treatment.
Refraction
Refraction helps determine the exact prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses. The eye doctor uses a device called a phoropter. You will look through different lenses to determine which one gives the clearest vision.
The doctor will ask you to compare two lenses and say which one is clearer. This process is repeated with various lens combinations. Refraction helps measure the degree of astigmatism. It identifies how light focuses on the retina. The result is a precise prescription for correcting your vision.
Corneal Topography
Corneal topography maps the surface of the cornea. This test provides a detailed image of the cornea’s shape. You will look into a special camera that captures the cornea’s surface. The resulting map shows any irregularities in the cornea’s curvature.
Corneal topography is particularly useful for diagnosing complex cases of astigmatism. It helps the eye doctor understand the extent of the astigmatism. This test is also helpful in planning treatments like contact lenses or surgery.
5 Astigmatism Treatment Options
Astigmatism treatment varies based on the type and severity.
For myopic and hyperopic astigmatism, eyeglasses and contact lenses are common solutions. For mixed astigmatism, more specialized lenses might be needed. In some cases, gas-permeable or hybrid lenses provide better correction. Refractive surgeries like LASIK or PRK can also be options for all types of astigmatism. These surgeries reshape the cornea to correct its focusing power.
Choosing the right astigmatism treatment depends on various factors. These include the severity of your astigmatism, your lifestyle, and your overall eye health. Regular eye exams are crucial to monitor astigmatism symptoms and ensure your treatment is effective. Discussing your options with an eye doctor will help you make an informed decision.
Here are the most common treatments for astigmatism:
Eyeglasses to Treat Astigmatism
Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest way to correct astigmatism. They are easy to use and effective. Eyeglasses with special lenses can help focus light properly on the retina. These lenses are designed to correct the irregular shape of the cornea or lens.
Wearing eyeglasses can reduce astigmatism symptoms like blurred vision and eyestrain. Regular eye exams ensure your prescription is up-to-date.
Contact Lenses to Address Astigmatism
Contact lenses are another option for astigmatism treatment. They sit directly on the eye and provide clear vision. There are different types of contact lenses available:
- Toric Lenses: These lenses have different powers in different meridians to correct astigmatism. They are designed specifically for the unique shape of myopic eyes.
- Gas-Permeable Lenses: These lenses are rigid and provide sharper vision for people with higher degrees of astigmatism. They allow oxygen to pass through, which is healthy for the eyes.
- Hybrid Lenses: These lenses have a gas-permeable center and a soft outer ring. This combination provides comfort and clear vision.
Contact lenses can offer more natural vision than eyeglasses. They move with your eyes, providing a wider field of view.
Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) as A Solution for Astigmatism
Orthokeratology, or Ortho-K, is a non-surgical astigmatism treatment. It involves wearing rigid contact lenses overnight. These lenses reshape the cornea temporarily, providing clear vision during the day. Ortho-K can reduce the need for eyeglasses or contact lenses during waking hours.
However, the effects are not permanent. You need to wear the lenses regularly to maintain clear vision. Ortho-K is suitable for mild to moderate astigmatism.
Laser Surgery for Astigmatism
Laser surgery is a popular option for astigmatism treatment. Procedures like LASIK and PRK can reshape the cornea to correct astigmatism. LASIK involves creating a thin flap in the cornea and reshaping the underlying tissue with a laser. PRK reshapes the cornea’s surface without creating a flap. These procedures are effective for mild to moderate astigmatism.
Laser surgery can provide long-lasting results. However, it may not be suitable for everyone. Your eye doctor will perform an astigmatism test to determine if you are a good candidate.
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) Procedure to Treat Astigmatism
Refractive Lens Exchange (RLE) is a surgical procedure that replaces the eye’s natural lens with an artificial one. It is usually recommended for people with severe astigmatism or other refractive errors.
RLE can correct astigmatism and reduce the need for eyeglasses or contact lenses. The artificial lens is chosen based on your specific vision needs. RLE is similar to cataract surgery but is performed for refractive purposes.
5 Practical Tips for Living with Astigmatism

Living with astigmatism can be challenging, but there are ways to manage it. Managing astigmatism involves a combination of regular care and lifestyle adjustments.
Here are some tips to help you cope with astigmatism. By following these tips, you can reduce astigmatism symptoms and maintain better vision.
Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are crucial for managing astigmatism. An eye doctor can monitor your astigmatism symptoms and check for changes in your vision. They will perform an astigmatism test to update your prescription if needed. Regular check-ups ensure your eyeglasses or contact lenses provide the best correction. It’s important to see your eye doctor at least once a year.
Proper Lighting
Good lighting can reduce eyestrain, which is important for people with astigmatism. Make sure your work and reading areas are well-lit. Proper lighting helps your eyes focus better, reducing the strain on your astigmatism vision. Avoid working or reading in dim light. Use adjustable lamps and position them so that light does not cause glare on your screen or book.
Computer Use
Spending a lot of time on the computer can worsen astigmatism symptoms like eyestrain and headaches. To manage this, take regular breaks. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. This simple habit can reduce eyestrain. Also, make sure your screen is at eye level and a comfortable distance. Adjust the brightness and contrast to reduce glare.
Healthy Diet
A healthy diet supports overall eye health, which is important for managing astigmatism. Include foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Vitamins A, C, and E are especially beneficial for eye health. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish can also help. Leafy greens, carrots, citrus fruits, and nuts are great choices. Staying hydrated is also important for eye health.
Protect Your Eyes
Protecting your eyes from damage is crucial when living with astigmatism. Wear sunglasses to shield your eyes from harmful UV rays. This can prevent additional eye strain and potential damage. If you play sports, use protective eyewear. This helps prevent injuries that could worsen your astigmatism. Choose sunglasses with 100% UV protection and wear them even on cloudy days.
Regular eye exams, proper lighting, and eye protection are key. A healthy diet and good computer habits also support eye health. With the right approach, living with astigmatism can be manageable.
4 Myths About Astigmatism
There are many myths about astigmatism. Let’s clear up some common misconceptions:
Astigmatism Only Affects Adults
False. Astigmatism can affect people of all ages, including children. Many children are born with astigmatism. If left untreated, it can lead to problems in school. Kids might have trouble reading or focusing on the board. Regular eye exams can catch astigmatism early.
Early detection means early treatment. Eyeglasses or contact lenses can help correct vision in children with astigmatism.
Astigmatism Gets Worse with Age
Not necessarily. Astigmatism can change over time, but it does not always worsen. Some people may notice changes in their astigmatism as they get older. However, these changes are often slight. Regular eye exams can help monitor any changes.
If astigmatism symptoms become bothersome, adjustments in treatment can be made. Eyeglasses, contact lenses, or even surgical options can be considered as needed.
Only Surgery Can Correct Astigmatism
False. Surgery is not the only option for correcting astigmatism. Eyeglasses are a simple and effective solution. They are safe and easy to use. Contact lenses are another good option. There are special lenses designed for astigmatism, like toric lenses.
These lenses help correct the irregular shape of the cornea. Surgery is an option but not always necessary. Treatments should be tailored to the individual’s needs.
Astigmatism is Caused by Reading in Dim Light
False. Astigmatism is not caused by reading in dim light. It is usually due to the shape of the cornea or lens. The cornea or lens may be more curved in one direction. This irregular shape leads to blurred or distorted vision. Genetics often play a role in astigmatism.
If your parents have it, you might have it too. Reading in dim light can cause eyestrain but not astigmatism. Proper lighting is important for comfort but does not affect the shape of the cornea.
Conclusion
Here’s a concise conclusion for the blog using the key keywords:
Astigmatism may sound tricky, but it’s nothing to fear. Regular eye check-ups are key to spotting astigmatism symptoms early. An astigmatism test is quick and easy, helping your eye doctor find the best solution for you.
Whether it’s glasses, contacts, or other treatments, there are many ways to improve astigmatism vision. With the right care, you can see clearly and comfortably. Remember, astigmatism treatment is all about finding what works best for you.
Don’t let blurry vision hold you back. If you have astigmatism, book an eye exam today. Clear vision is just an appointment away!




